Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard application programming interface (API) designed for accessing database management systems (DBMS). After creating a new data source through the Windows ODBC Data Source Administrator, Micromine Origin & Beyond (MMOB) can communicate with that data source and retrieve the data. This subject might appear intimidating if you're not well-acquainted with it (I say this from personal experience), but it doesn't need to be. This article will give a brief explanation of ODBC data sources, show how to create a new data source, access the data source from MMOB and append an SQL clause.
ODBC Data Sources - Why and How?
ODBC was created for the main purpose of providing easy access to different DBMSs using a single software interface. Without ODBC, consider the development required to ensure MMOB was compatible with every single database software on the market. For this to work, DBMS developers release an ODBC driver with their software. The driver essentially acts as a translator between MMOB and the associated DBMS using Structured Query Language (SQL).
The ODBC environment consists of three ingredients: 1) ODBC-compliant software (MMOB), 2) ODBC driver manager (ODBC Data Source Administrator on Windows) and 3) ODBC driver. When these are configured, you can import or link to data within a DBMS.
Creating a New Data Source
There are two ways to create a new data source: 1) through the ODBC Data Source Administrator app in Windows or 2) by clicking New... on the Select Data Source... dialog in MMOB.
ODBC Data Source Administrator
This app can be opened by searching for ODBC in the Windows search bar and then clicking on ODBC Data Sources. On the User DSN tab, click Add... to begin creating a data source. Select the appropriate driver and click Finish to enter the Setup window.
In this example, I am setting up an Access Database. The Access driver requires the user to name the data source and then navigate to an Access Database file (*.mdb, *.accdb) through the file directory. After selecting the database, finalise the setup by pressing OK. Note: Each driver has a different set-up process (e.g. for databases located on a server, you will be asked to connect to a server instead of finding a database file.)
MMOB Dialog
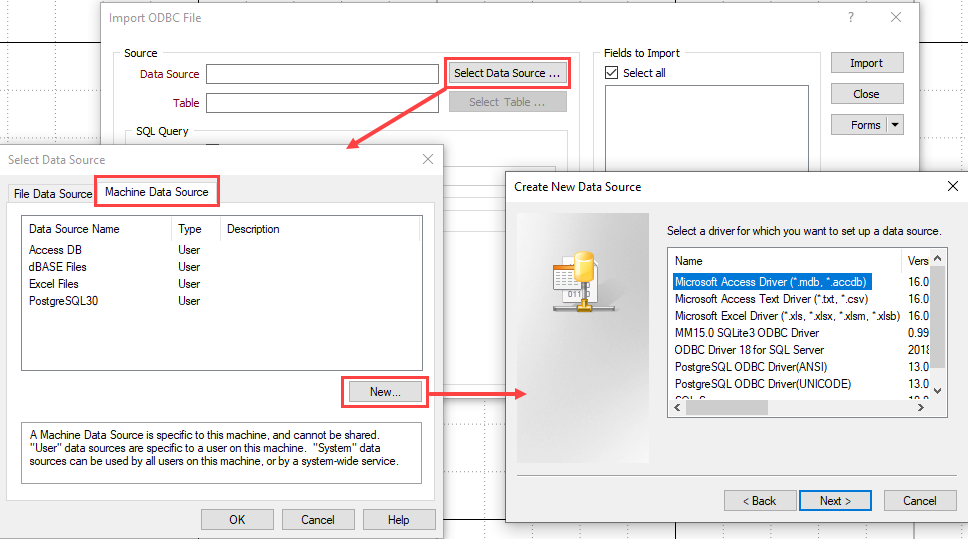
To set up a data source within MMOB, you simply navigate to Select Data Source... > Machine Data Source > New.... This will open up the driver selection dialog as we saw in the previous method. From here, it is exactly the same process as using the ODBC Data Source Administrator.
Accessing The Data
Open the Import ODBC tool (File | Import | ODBC). Optionally, you can use the ODBC Link tool (File | Data File | Link | ODBC); the process is the exact same, however, the link tool will create ODBC link files (.DDL) instead of Micromine files (.DAT).
Press Select Data Source... and navigate to the Machine Data Source tab. Select the data source you would like to access then select a data table from that source.
After naming/selecting the target file, choose a structure option. These options handle how the file will be structured when the data is imported (i.e. field types, widths, etc.).
Determine structure: If this option is selected, the function will read the contents of the source table to determine the most appropriate width and format for each field in the target file.
Use database structure: If this option is selected, the function will base the structure of the target file on the structure of the source table.
Use current structure: If this option is selected, the function will use the current structure of the target file.
Afterwards, configure the fields you want to import; you may choose to import all fields (default) or only a number of select fields. Lastly, you can choose to preview the import before it is executed. With this option selected, an import preview dialog will open after pressing Import. In this dialog, you can review the structure of the file and make any changes before confirming the import.
SQL Queries (Optional)
SQL is the programming language used by ODBC to communicate with your database. When the import/link form is run, a SELECT FROM statement is generated by the software, whereby the chosen table in the data source is accessed. Appending a clause to the SQL statement allows for filtering or ordering of the imported data. Any valid SQL clause(s), such as WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY etc., or a combination thereof, can be appended to the SELECT FROM statement.
For example: I have a database that contains drilling data for multiple sites, however, I only want to import data related to Site A. To do this, I will append the clause WHERE site_id = 'Site A'. This will filter the database and only import the data in Site A. You can read more on our webhelp article: SQL Clauses
Want to learn more?
Click here to login to our Learning Management System
Click here to request access

Comments
0 comments
Please sign in to leave a comment.